Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ishii, Eiichi
Environmental Earth Sciences, 83(3), p.98_1 - 98_15, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.04(Environmental Sciences)The long-term geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste relies on predictions of future changes in a disposal facility's hydro-mechanical characteristics to assess potential leakage through fractures in the excavation damaged zone (EDZ) after backfilling the facility. This study evaluated the transmissivity of EDZ fractures using in situ hydraulic tests around the area of a full-scale, experimental, engineered barrier system in the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, Hokkaido, Japan. After their installation, the buffer blocks swelled, altering the stresses within the EDZ fractures. The effects of these changing stresses on the fractures' transmissivity were assessed over a period of 4 years. The transmissivity continuously decreased in this period to about 41% of its value measured prior to the swelling. Using the Barton-Bandis normal-stress-dependent fracture-closure model, the decrease in transmissivity is quantitatively attributed to closure of the EDZ fractures, which was caused by the swelling pressure increasing up to 0.88 MPa. Evidence of fracture closure came from seismic tomography surveying, which revealed a slight increase in seismic velocity in the study area with increasing swelling pressure. The results show that EDZ fractures were closed by swelling of the full-scale buffer material. They also demonstrate the applicability of the Barton-Bandis model to preliminary estimation of the long-term transmissivity of EDZ fractures in facilities for the geological disposal of radioactive waste.
Sasagawa, Tsuyoshi; Mukai, Masayuki; Sawaguchi, Takuma
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-012, 122 Pages, 2022/01
Reducing public dose is required when radioactive wastes such as high-level and from reactor core internals etc. are disposed of by means of multi barrier system consist of engineered and natural barriers. In these barriers, engineered barrier is expected to bring out confinement function of waste's radionuclides in the barrier. Materials used as the engineered barriers are altered and performances of the barrier materials are degraded in course of time. To estimate properly the degraded performances, analytical evaluation of long-term change of the engineered barrier state is important. Change state of the engineered barrier is given by mass-transport and geochemical-reaction inside the barrier materials and these phenomena are interrelated, it is necessary to calculate the state by means of coupled analysis procedure. We have developed a coupled mass-transport and geochemical-reaction calculation code (MC- BUFFER) to evaluate alteration of engineered barrier specially targeted for water permeability of bentonite buffer material as one of most important performances to engineered barrier. This report describes functions expected for the engineered barrier, influence parameters for the functions, implementation models in MC-BUFFER, structure and functions of MC-BUFFER, input file format and output examples, execution method of MC-BUFFER, and sample run with MC-BUFFER.
Murakami, Hiroaki; Ashizawa, Masaomi*; Tanaka, Kazuhiro*
Oyo Chishitsu, 59(1), p.2 - 12, 2018/04
This study describes the features of fractures and their fillings along with the long-term behavior of their hydrogeological structures in an underground environment based on the results of a geological investigation conducted at an underground facility in northern Kyushu. Fractures were classified into five groups on the basis of fracture orientation: A, B, C, D, and low-angle groups. The genesis of all fractures is the cooling process of granodiorite pluton. Almost all of the water-conducting fractures are included in the B group. Because a number of fracture fillings in the B group are filled by prehnite and crushed fragments of epidote and quartz, the fractures in this group alternated sealing and re-opening. The fracture characteristics in the B group are follow as: accompanying many alteration halos, long trace length, and cutting off other fractures. These results indicate that fractures in the B group have possibly functioned as pathways for groundwater flow in the long term.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Nago, Makito*
Jiban Kogakkai-Shi, 65(8), p.12 - 15, 2017/08
In this paper, we described the development of the supporting tool of observational construction of the underground research laboratory, and the monitoring result of hydro-mechanical properties around the gallery wall. As an observational construction tool, we developed a "3D geological structure/construction data visualization system". The geological data, measurement data, construction data, and prediction analysis results are visualized and integrated comprehensively as the construction proceeds. The planned support pattern was examined according to the visualized data. In addition, the Excavation Damaged Zone (EDZ) was extended within 1.0 m from the gallery wall. In this area, hydraulic conductivity was enhanced. However, the extent of the EDZ was not enlarged along with time; the stability of the support was also confirmed on the basis of the measurement of stress in the shotcrete. Integrating these results the observational construction considering the development of an EDZ can be established. This technology will have an important role in geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ishii, Eiichi; Nakayama, Masashi; Fujita, Tomoo
Nihon Zairyo Gakkai Dai-65-Ki Tsujo Sokai, Gakujutsu Koenkai Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), p.19 - 20, 2016/05
no abstracts in English
Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Onoe, Hironori; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Abumi, Kensho*; Hashimoto, Shuji*; Bruines, P.*
JAEA-Research 2015-011, 59 Pages, 2015/10
It is important to evaluate groundwater flow characteristics on several spatial scales for assessment of long-term safety on geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes. An estimation of hydraulic heterogeneity caused by fracture network is significant for evaluation of the groundwater flow characteristics in the region of tens of meters square. Heterogeneity of equivalent hydraulic properties is needed to estimate for evaluation of the groundwater flow characteristics in the region of several km square. In order to develop the methodology for multi-scale hydrogeological modeling taking into account the hydraulic heterogeneity, spatial distribution of fractures and their hydraulic properties have been modeled using discrete fracture network (DFN) model. Then, hydrogeological continuum model taking into account the hydraulic heterogeneity has been estimated based on the DFN model. Through this study, the methodology for multi-scale hydrogeological modeling according to type of investigation data has been proposed.
*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2001-007, 56 Pages, 2002/01
In the geological disposal concept of radioactive wastes, a kind of clay with sorption ability and low permeability, called bentonite, is envisaged as an engineered barrier system in the geological repository. Also, the cemetitious material is envisaged as the backfill material in the vaults and the structure material of the vaults. The groundwater in contact with the cementitious material will promote hyperalkaline conditions in the repository environment and these conditions will affect the performance of the bentonite. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the interaction between the cementitious material and the bentonite for the evaluation of long term stability of the disposal system. In this study, for the identification and the investigation of the secondary minerals, the batch immersion experiments of the powder bentonite were carried out using synthetic cement leachates (pH=7, 12.5, 14) at 200 C. As the results, it was confirmed that Na as exchangeable cations in the bentonite can exchange relatively easily with Ca in the solution from the experiment results. And the ratio of cation exchange was estimated to be about 25% based on the amount of exchangeable cations Ca
C. As the results, it was confirmed that Na as exchangeable cations in the bentonite can exchange relatively easily with Ca in the solution from the experiment results. And the ratio of cation exchange was estimated to be about 25% based on the amount of exchangeable cations Ca between layers. Furthermore, it was concretely shown that the generation of analcime might be affected by the Na concentration from results of the solution analyses and a stability analysis of analcime using the chemical equilibrium model, in addition to the pH in the solution.
between layers. Furthermore, it was concretely shown that the generation of analcime might be affected by the Na concentration from results of the solution analyses and a stability analysis of analcime using the chemical equilibrium model, in addition to the pH in the solution.
*;
JNC TN8430 2001-006, 65 Pages, 2001/10
We had been conducted to study hydraulic permeability along fracture intersection by NETBLOCK system using natural rock specimen. Since the permeability of this rock specimen fracture is high, it was suggest that turbulent flow might be occurred in available range of measurement system. In case of turbulent flow, estimated permeability and fracture aperture from test data tend to be low. Therefore we should achieve laminar flow. This study was used the high viscosity liquid instead of water, and test conditions which could attain laminar flow with the rock specimen was examined. The rock specimen is granite rock, has natural Y-type fractures intersection. A solution of Methyl-cellulose is used as high viscosity liquid. Due to the high viscosity liquid, hydraulic head could be measured in the wide range, and high viscosity liquid improved the accuracy of measurement. Laminar flow could be achieved in the rock specimen by the high viscosity liquid over 0.1wt%.
Uchida, Masahiro; Yoshino, Naoto
JNC TN8410 2001-016, 36 Pages, 2001/05
This technical report summarizes sampling of the natural rock including conductive fracture. Hydraulic test was conducted at the target fracture prior to excavation. Objective of the sample was to reproduce same transmissivity at LABROCK by adjusting normal stress. This report was originally compiled by PNC in october, 1993.
Uchida, Masahiro; Yoshino, Naoto
JNC TN8410 2001-015, 35 Pages, 2001/05
This technical report summarizes excavation and preparation of the natural rock block sample used in LABROCK. This report was originally compiled by PNC in March, 1993.
*; Kanazawa, Yasuo*;
JNC TN8400 2001-012, 69 Pages, 2001/04
On understanding the radionuclide transport in natural barrier in radioactive waste isolation research, the macroscopic dispersion in heterogeneous permeability field in the underground rock is regarded as an important process. Therefore, we have conducted lots of tracer experiments by the MACRO II facility with an artificially constructed heterogeneous permeability field. In order to study the scale dependence of dispersion coefficients in case of laboratory experiments, we placed the flow cell horizontally, and conducted injection-withdraw tracer experiment with a single well. We have conducted I5 cases experiments. These cases were prepared by changing a position of single well and the injection-withdraw time. At each position we have conducted 9 cases and 6 cases experiments. In this report, we evaluated the macroscopic dispersion coefficients by the fitting of analytical solution to breakthrough curve measured by the 15 cases pumping tracer experiment. Consequently, we could evaluate the dispersion coefficients for 12 cases of 15 cases. Then, we discussed the relation between a injection-withdraw flow rate and a property of heterogeneous media and dispersion coefficient. The conclusions obtained from the results of the evaluation are summarized as follows, (1)It was found that the macroscopic dispersion coefficients tend to be increased with increase of the average radius of tracer front spread around a single well. (2)We have conducted any experiments with s single well settled at two positions. In case of that there is low permeability around a single well, we found dispersion coefficients are large. In case of that there is high permeability around a single well, we found dispersion coefficients are small. (3)In three cases that we could not evaluate because of incorrect accuracy of fitting, we have found it possible that there is some points that dispersion coefficients were strikingly small in tracer front.
*; *;
JNC TN8430 2001-003, 64 Pages, 2001/03
Handling methods and test conditions of hydraulic tests for NETBLOCK system had been examined by using acrylic and/or artificial rock specimen. A natural rock specimen (granite : excavated from Kamaishi mine) with fracture intersection was formed into practicable size for NETBLOCK system. Recently, we conducted a series of hydraulic test, in order to study the influence of fracture intersection by using the natural rock specimen. Hydraulic tests were conducted under several centimeters of head, which could be controlled by improved system because hydraulic permeability of target fractures were high. As a result, 10
 10
10 (m
(m /s) orders of hydraulic transmissivity of target fractures could be measured. A low permeability in the NW direction at the lower fracture was estimated from the heterogeneous head distribution. However, it is also expected that turbulence flow might be occurred under this study condition because fracture permeability is high and flow rate through the fracture is relatively high. In case of turbulence-flow, an estimated hydraulic transmissivity is low. High-viscosity fluid hydraulic test to achieve laminar flow will be needed for correcting an evaluated transmissivity.
/s) orders of hydraulic transmissivity of target fractures could be measured. A low permeability in the NW direction at the lower fracture was estimated from the heterogeneous head distribution. However, it is also expected that turbulence flow might be occurred under this study condition because fracture permeability is high and flow rate through the fracture is relatively high. In case of turbulence-flow, an estimated hydraulic transmissivity is low. High-viscosity fluid hydraulic test to achieve laminar flow will be needed for correcting an evaluated transmissivity.
; *
JNC TN8400 2001-010, 25 Pages, 2001/03
Performance assessment in geosphere for the JNC's 2nd progress report was based on nuclide migration calculation results by discrete fracture network model. The channel network model approximated from fracture network model with considering fracture connectivity was applied for nuclide migration analysis, since fracture network model had too large data to calculate nuclide migration. However, there are many options in the process of approximation from fracture network model to channel network model. In case of analyzing nuclide migration for above report, so-called "base case", one option was chosen from many options, arbitrarily. In this report, the sensitivity of these options to nuclide migration calculation results was studied. As a result, there was no significant impact to nuclide migration although connectivity of channel and flow characteristics of the model slightly changed among different options. Based on above studies, we concluded that an option used for the base case was appropriate.
*; *; Morooka, Koichi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-043, 170 Pages, 2000/03
This study is an object to collect and arrange data about the mass transfer path during a natural barrier system by grasping actual rock feature, in order to be useful for a performance assessment of a natural barrier system at geological disposal of HLW. An existence of permeability high large-scale faults extends a large influence over a performance assessment of geological disposal. With "The Second Progress Report on Research and Development for the Geological Disposal of HLW in Japan" which Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) issued, it is as" A repository would be located at least 100 meters away from major faults and major fracture zones which could adversely affect the stability and performance of the repository" as a Reference Case concept model of a natural barrier system, Then, they are as "in the Reference Case, the transport path consists of the host rock and the downstream fault". It will not be easy to know the distribution of faults in the subsurface deep division without data acquired from many boreholes and underground laboratory. With this study, specific data on the large-scale faults and fracture zones has been collected and arranged by investigating in underground galleries and on the literatures of a post-operated mine site. Based on this result, a consideration on the principal transfer pass at a natural barrier system has been conducted. The contents conducted in this report is the follows. (1)investigation of literature about data of fracture, shear zone, and geology, (2)field investigation of fracture and shear zone in the rock, (3)arrangement of these results, (4)modeling of the major water conductive feature, and (5)evaluation of an assumption which has been introduced in the Second Progress Report issued by JNC.
Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; TRAN DUC PHI OAN*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-056, 487 Pages, 2000/02
JNC presented the 2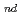 progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named TRAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named TRAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; TRAN DUC PHI OAN*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-055, 49 Pages, 2000/02
JNC presented the 2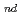 progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named THAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named THAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.